Have you ever wondered how people can afford to buy a house? Well, one big reason is something called a mortgage. It’s like a special kind of loan that helps you buy a home, even if you don’t have all the money upfront.
In America, people owe a total of $12.14 trillion on 84.0 million mortgages. That’s about $144,593 for each person who has a mortgage. Mortgages make up 70.2% of all the money people owe in the country.
Also, Americans owe $349 billion on 13.1 million home equity lines of credit (HELOCs). That’s around $26,702 for each account. HELOC debt makes up 2.0% of all the money people owe in the U.S.
What Is a Mortgage?

According to Warren Buffett “A mortgage is a tool that allows individuals to leverage their assets to acquire property or real estate. It’s like a financial bridge that connects dreams of homeownership to reality, but one must tread carefully to ensure it doesn’t become a burden.”
To get a mortgage, you apply to a bank or lender and meet certain conditions, like having a good credit score and being able to make a down payment. The bank checks your application carefully before giving you the loan. There are different types of mortgages, like regular ones or ones with fixed rates, depending on what you need.
How Mortgages Work
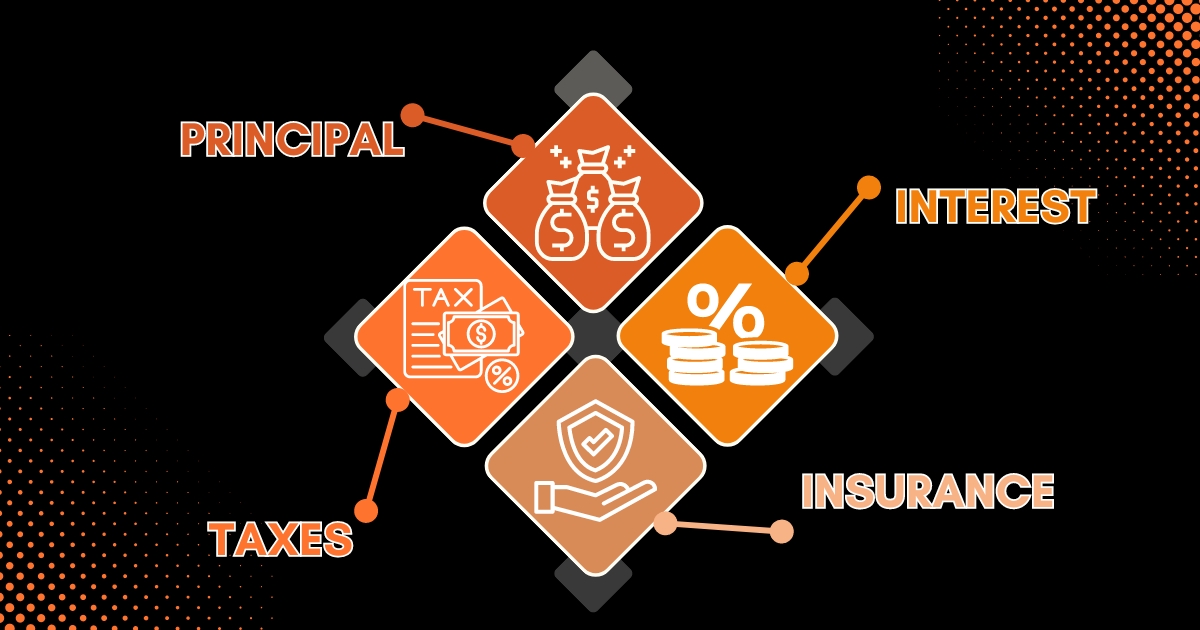
Each month when you make a mortgage payment, it’s divided into four parts known as principal, interest, taxes and insurance or PITI:
- Principal: This reduces the amount you owe on your loan.
- Interest: This is the fee charged by your lender for borrowing the money.
- Taxes: Each month, you pay a portion of your annual property taxes based on your neighborhood’s assessed value.
- Insurance: Lenders need you to have homeowners insurance to protect your home from risks like fire or theft. You might also pay mortgage insurance based on your down payment or loan type.
Initially, you pay mostly interest on your loan, but as time goes on, more of your payment goes toward paying back the loan itself. Your lender will give you a schedule that shows how your loan amount goes down and how much you pay in principal (the loan amount) versus interest each month.
If you are a business owner, an investor, have assets and not income, or anyone else who doesn’t fit in the box, don’t fret! There are mortgage options available for you. We recently helped a client who had bought a duplex in cash, renovated one half, and moved in, renting out the other half. We helped her be able to get out the money she used from her assets a short few months prior to, plus use the new value of her home. For this house hacking minded homeowner this allows her to scale and look towards the next real estate investment opportunity.
5 Traditional Types of Mortgages
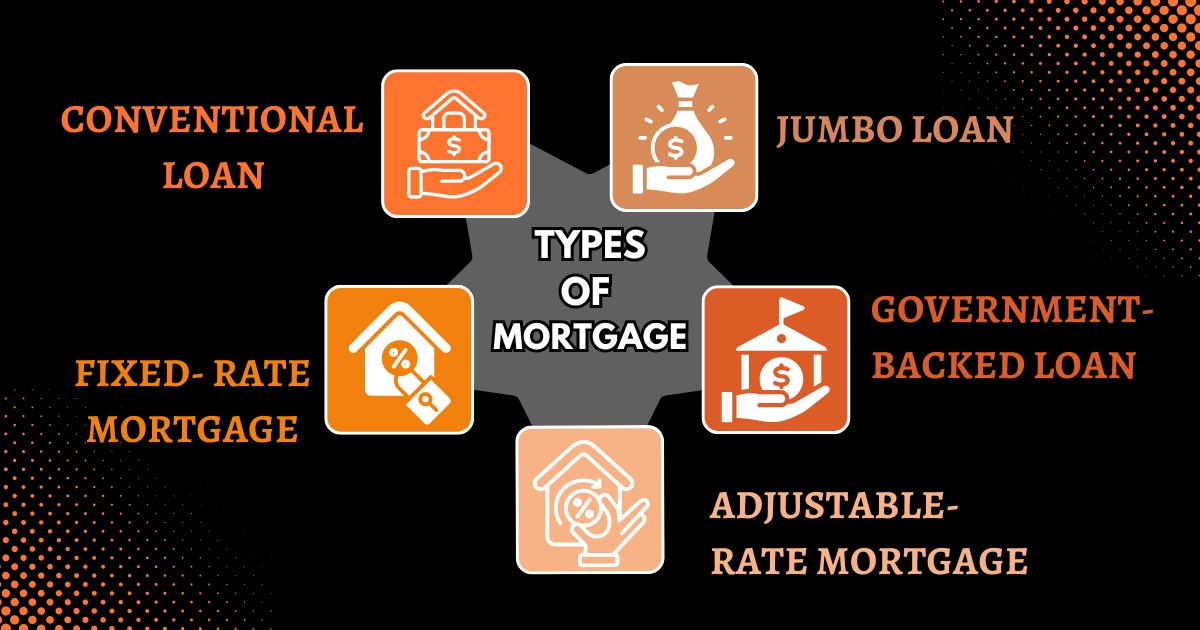
Many of us require a mortgage to purchase a home, but not all mortgages are the same. To assist you in finding the best home loan for you, here’s our guide to the five main types of mortgages.
1. Conventional Loan
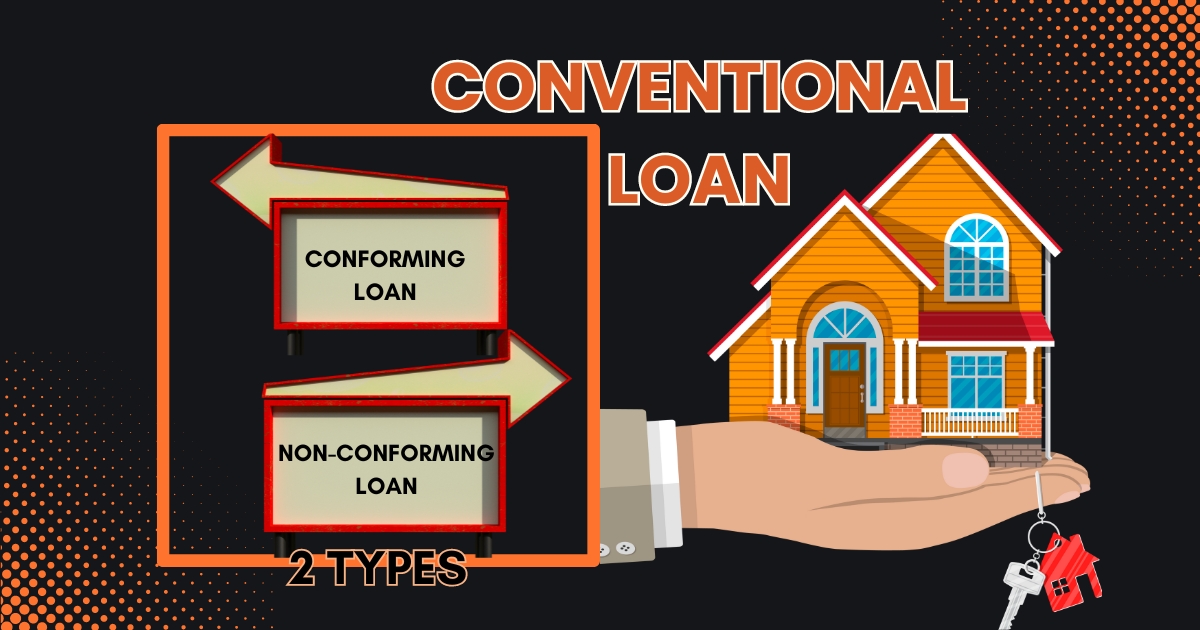
Conventional loans, which are the most common type of mortgage, come in two types: Conforming and Non-Conforming.
- Conforming: A regular loan follows rules from the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA). These rules cover things like credit, debt, and how big the loan can be. If a normal loan follows these rules, big companies like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac can buy it. They’re like big helpers in the mortgage world.
- Non-Conforming: These loans don’t follow all of the FHFA’s rules. One common irregular loan is a jumbo loan, which is a really big mortgage that’s more than what regular loans allow. Big companies can’t buy irregular loans, so they’re a bit riskier for lenders.
Pros of Conventional Loans |
Cons of Conventional Loans |
| Most lenders offer it | You need a credit score of at least 620 to qualify. |
| You can use it to buy your main home, a vacation home, or even a rental property | Your debt should be lower compared to your income than with other mortgages. |
| You can pay as little as 3% for a regular, fixed-rate loan | If you’re not paying at least 20% upfront, you’ll need to pay more for private mortgage insurance (PMI). |
2. Jumbo Loan

Jumbo mortgages are large home loans that exceed the usual government limits. For instance, in 2024, this means any loan over $766,550, or $1,149,825 in pricier areas. Because these loans are too big for the government to purchase, and they can carry more risk.
Pros of Jumbo Loans |
Cons of Jumbo Loans |
| Can help buy a pricier house. | Not all lenders offer it. |
| Has rates that compete well with regular loans now. | You need a higher credit score, usually around 700 or more. |
| It’s the only option in areas where houses are very expensive. | You need to pay more money upfront, usually around 10% to 20%. |
3. Government-backed Loan

The U.S. government doesn’t lend mortgages, but it helps more Americans buy homes by supporting three main types of mortgages.
FHA loans: FHA loans are for people with lower credit scores, even as low as 500. You need a down payment, but it’s smaller, starting at 3.5%. Yet, you must pay extra for insurance to protect the lender if you can’t pay. Also, there’s a cap on how much you can borrow.
VA loans: These loans are for military members and their families, backed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). You don’t need to put down a minimum payment, get mortgage insurance, or have a certain credit score. However, there’s a fee when you finalize the loan.
USDA loans: Backed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), these loans help low- to moderate-income borrowers purchase homes in rural areas. They don’t have strict credit score or down payment requirements, but there are fees associated with the guarantee.
Pros of Government-backedLoans |
Cons of Government-backedLoans |
| They’re more flexible about upfront payments and credit requirements. | You might need extra cash for FHA mortgage insurance, VA funding fees, and USDA guarantee fees. |
| This helps people who might not usually be able to get a loan to buy a house. | These fees are for buying a home in specific price limits set by FHA or in rural areas, or if you’re a service member. |
4. Fixed-Rate Mortgage
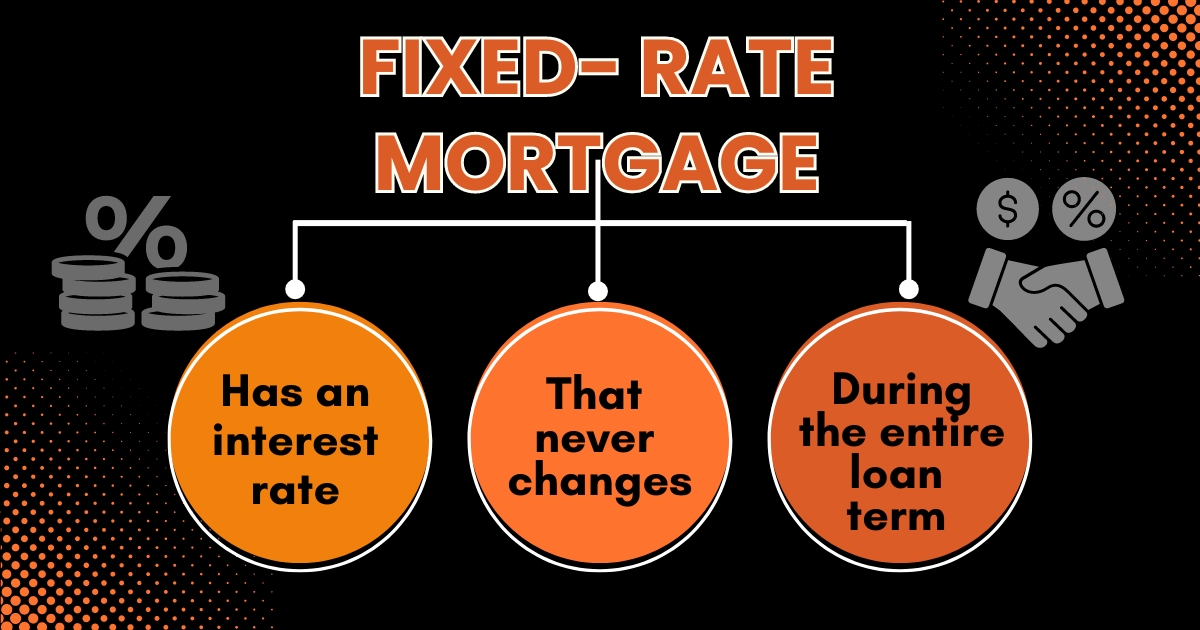
With fixed-rate mortgages, the interest rate you pay stays the same throughout the loan. This means your monthly payment, covering what you borrowed plus interest, remains constant. These loans typically last 15 or 30 years, but some lenders offer flexibility in repayment terms.
| Pros of Fixed-Rate Mortgages | Cons of Fixed-Rate Mortgages |
| Steady monthly mortgage payment | Rates on adjustable loans often start low but may go up later. |
| Easier to budget for | Have to get a new loan to pay less interest. |
5. Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM)
An adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) is different from a loan with a fixed rate because the interest rate can change. At first, you might have a low fixed rate for a set time. After that, the rate can go up or down now and then until you pay off the loan.
For example, a 5/6 ARM has a fixed rate for five years, then it changes every six months based on the economy. If the rate goes up, your monthly payment goes up too. If it goes down, your payment decreases.
Pros of ARMs |
Cons of ARMs |
| Rates start low | It’s harder to predict how much you’ll pay each month because the rates might go up. |
| You might pay less later if interest rates go down. | Making it tough to plan your budget. |
Explore Your Mortgage Options Now
The mortgage that suits you depends on what you prefer and your situation. Before choosing a loan, calculate how much money you need from the bank by adding up the costs to buy or refinance your home.
When you’re thinking about buying a house, there’s a lot to think about, like your credit score, how much money you make, how much you owe, and where the property is located. These things affect what kind of mortgage you can get. Send an email to find the best option for you. Or start your journey by filling out a no obligation loan application today.
Final Thoughts
Mortgages are important for buying homes, especially if you don’t have lots of money saved. There are different types of home loans to fit various situations, including ones backed by the government to help more people qualify for them.
Mortgages let you buy a home without needing all the money upfront, and they make up a big part of the country’s debt. They come in types like fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, as well as government-backed loans like FHA. Before you pick one, think about things like how much money you can put down, how long you plan to stay in the house, and what your budget is like.
FAQs
What Exactly Is A Mortgage?
A mortgage is a special kind of loan that helps you buy a home. Instead of paying all the money upfront, you borrow it from a bank or lender and pay it back over time.
How Does A Mortgage Work?
When you get a mortgage, the bank gives you money to buy a house. You pay back this money every month for many years. The payments include what you borrowed and extra money called interest.
What Are The Different Types Of Mortgages?
There are different mortgages. One is called fixed-rate. The interest rate stays the same. Another is adjustable-rate. The interest rate can change. There are also special mortgages, like FHA loans. They help people with less money for a down payment or lower credit scores.
How Do I Choose The Right Mortgage For Me?
Picking the best mortgage depends on your situation and what you like. Consider how much money you can pay upfront, how long you’ll be in the house, and your monthly budget. Talking to a mortgage lender or financial advisor can help you find the right choice.
Mortgage Maestro Group – NMLS #1838215










